Type 2 Collagen Supplement is gaining traction as a potential solution for joint health and beyond. This naturally occurring protein, a key component of cartilage, is now available in supplement form, promising a range of benefits from improved joint mobility to enhanced skin elasticity. But does the science support these claims? This in-depth analysis explores the efficacy, safety, and various forms of type 2 collagen supplements, guiding consumers toward informed choices.
From understanding its unique molecular structure and diverse sources to examining the available scientific research and potential side effects, this report provides a comprehensive overview of type 2 collagen supplementation. We’ll delve into the different types of supplements, their manufacturing processes, and crucial considerations for consumers seeking to improve their joint health and overall well-being.
Type 2 Collagen: A Deep Dive into Structure, Benefits, and Supplements
Type 2 collagen, a crucial component of cartilage, is gaining traction as a dietary supplement. This article explores its structure, benefits, various supplement forms, manufacturing processes, potential side effects, and the current scientific evidence supporting its use.
Type 2 Collagen: Structure, Function, and Sources
Source: com.my
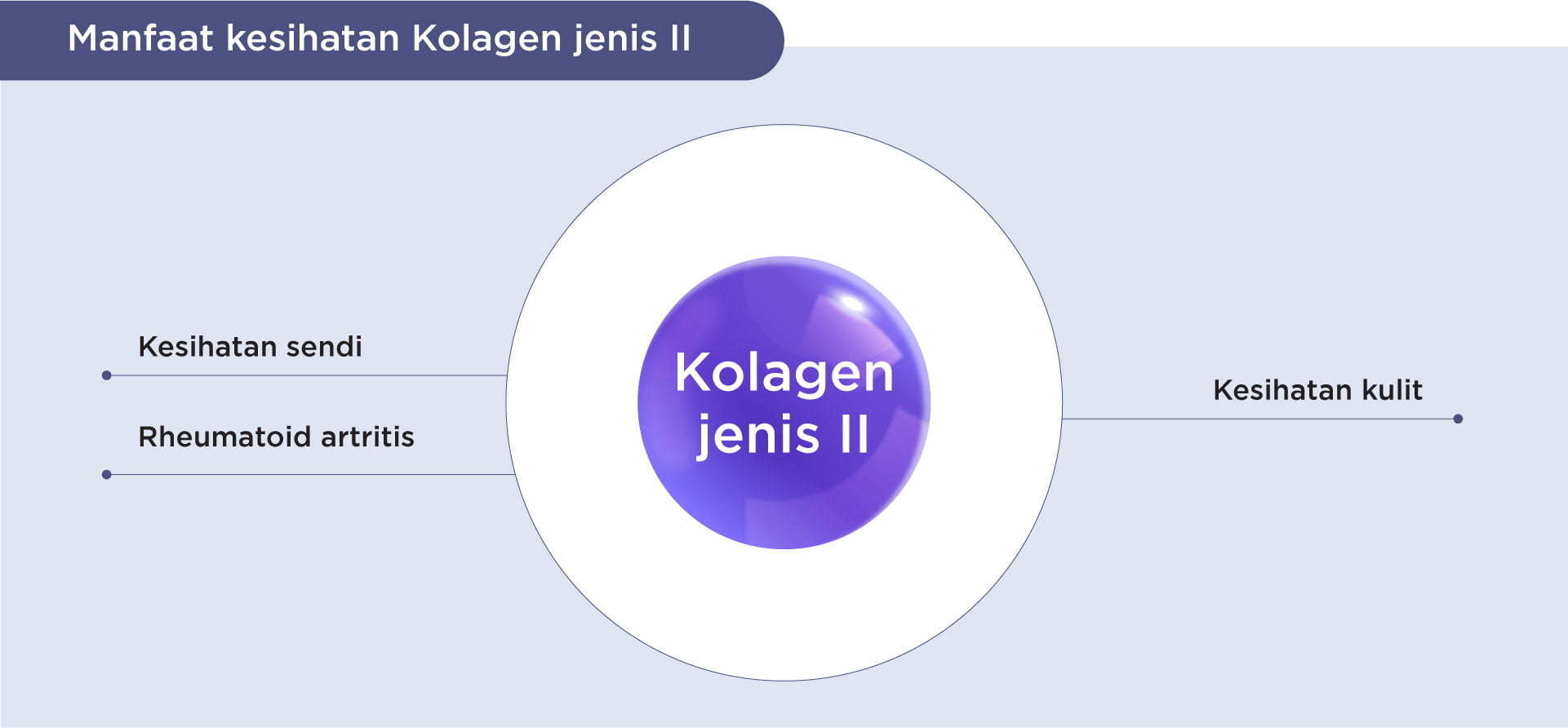
Type 2 collagen is a specific type of collagen, a major structural protein in the body. It forms a unique triple helix structure, comprised of three polypeptide chains intertwined. This structure provides the tensile strength and flexibility essential for cartilage function. Unlike type I collagen found in skin and bones, type 2 collagen is primarily found in cartilage, providing the cushioning and shock absorption necessary for joints.
Natural sources include chicken cartilage, and fish cartilage. The differences between type 2 and other collagen types lie primarily in their amino acid composition and resulting structural properties, influencing their roles in different tissues.
Benefits of Type 2 Collagen Supplements
Numerous potential health benefits are associated with type 2 collagen supplementation, primarily focusing on joint health and cartilage function. However, the evidence level varies across these benefits.
| Benefit | Mechanism | Evidence Level | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Joint Health | Stimulates cartilage regeneration and reduces inflammation | Moderate; some studies show positive effects, others inconclusive | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals |
| Reduced Joint Pain | Decreased inflammation and improved cartilage structure | Moderate; evidence suggests pain reduction in some individuals with osteoarthritis | Rarely reported, generally well-tolerated |
| Enhanced Skin Elasticity | May contribute to improved skin hydration and collagen production | Limited; more research is needed to confirm this benefit | Generally well-tolerated, but individual reactions may vary |
Type 2 collagen’s role in joint health is significant, as it supports the structural integrity and function of cartilage. Its potential contribution to skin health involves improved hydration and elasticity, though further research is warranted.
Types of Type 2 Collagen Supplements
Type 2 collagen supplements are available in various forms, including hydrolyzed and undenatured (native) collagen. Hydrolyzed collagen is broken down into smaller peptides, potentially improving absorption. Undenatured type II collagen, maintains its native triple helix structure. Bioavailability and effectiveness can vary between these forms, with some studies suggesting undenatured type II collagen may be more effective for stimulating specific immune responses relevant to joint health.
Typical dosages range from 40 to 80 mg daily, but optimal intake may vary based on individual needs and health conditions.
Supplement Ingredients and Manufacturing
Besides collagen, type 2 collagen supplements may contain additional ingredients such as fillers, flavorings, and preservatives. Manufacturing processes involve extraction, purification, and processing of collagen from natural sources. The purity and sourcing of collagen vary significantly across manufacturers.
| Manufacturer | Sourcing | Purity Claims | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer A | Chicken cartilage | 95% pure type II collagen | Hydrolysis and purification |
| Manufacturer B | Fish cartilage | 90% pure type II collagen | Low-temperature extraction |
| Manufacturer C | Chicken cartilage | 85% pure type II collagen | Enzymatic hydrolysis |
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Type 2 collagen supplements are generally considered safe, but potential side effects may include mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea or upset stomach. Interactions with medications are rare, but individuals with allergies to chicken or fish should exercise caution. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications.
- Mild gastrointestinal upset
- Potential allergic reactions (chicken or fish)
- Rarely reported interactions with medications
Scientific Evidence and Research
The scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of type 2 collagen supplements is growing, but more high-quality, large-scale studies are needed. Existing research suggests potential benefits for joint health, particularly in individuals with osteoarthritis. However, study designs and limitations vary, impacting the overall interpretation of findings. Future research should focus on standardizing supplement formulations, using robust study designs, and investigating long-term effects.
Type 2 collagen supplements are gaining popularity for their purported joint health benefits. However, understanding the long-term effects requires rigorous research, much like uncovering the full truth behind figures like Michael Franzese, whose story is detailed in the mobs most notorious informant the true story of michael franzese. Just as Franzese’s life reveals layers of complexity, the impact of Type 2 collagen on the body remains a subject of ongoing scientific investigation.
Consumer Considerations and Recommendations
Choosing a high-quality type 2 collagen supplement involves considering factors such as the source of collagen, purity levels, and manufacturing process. Look for supplements from reputable manufacturers with transparent labeling and third-party testing. Incorporate type 2 collagen supplements as part of a holistic approach to joint health, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Collagen Structure: A Molecular Perspective
Type 2 collagen’s unique triple helix structure is formed by three polypeptide chains, each composed of a repeating amino acid sequence, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These chains intertwine to create a robust yet flexible structure, essential for the tensile strength and elasticity of cartilage. Imagine three intertwined strands of rope, each strand representing a polypeptide chain. The glycine residues are crucial for the tight packing within the triple helix, while proline and hydroxyproline contribute to the helix’s stability and resistance to deformation.
Ending Remarks: Type 2 Collagen Supplement
Type 2 collagen supplements offer a promising avenue for improving joint health and potentially benefiting skin elasticity. While research continues to evolve, the existing evidence suggests potential benefits for individuals seeking to support their musculoskeletal system. However, it’s crucial to choose high-quality supplements from reputable manufacturers, consult with healthcare professionals, and be aware of potential side effects before starting any supplementation regimen.
Making informed decisions based on the available scientific evidence is key to maximizing potential benefits and minimizing risks.
